Understanding Reverse Stock Split: What You Need To Know
Reverse stock split is a corporate action that can significantly impact investors and the value of their shares. In the world of finance, understanding the dynamics of reverse stock splits is crucial for making informed investment decisions. This article will explore what reverse stock splits are, why companies opt for them, and how they can affect both the company and its investors.
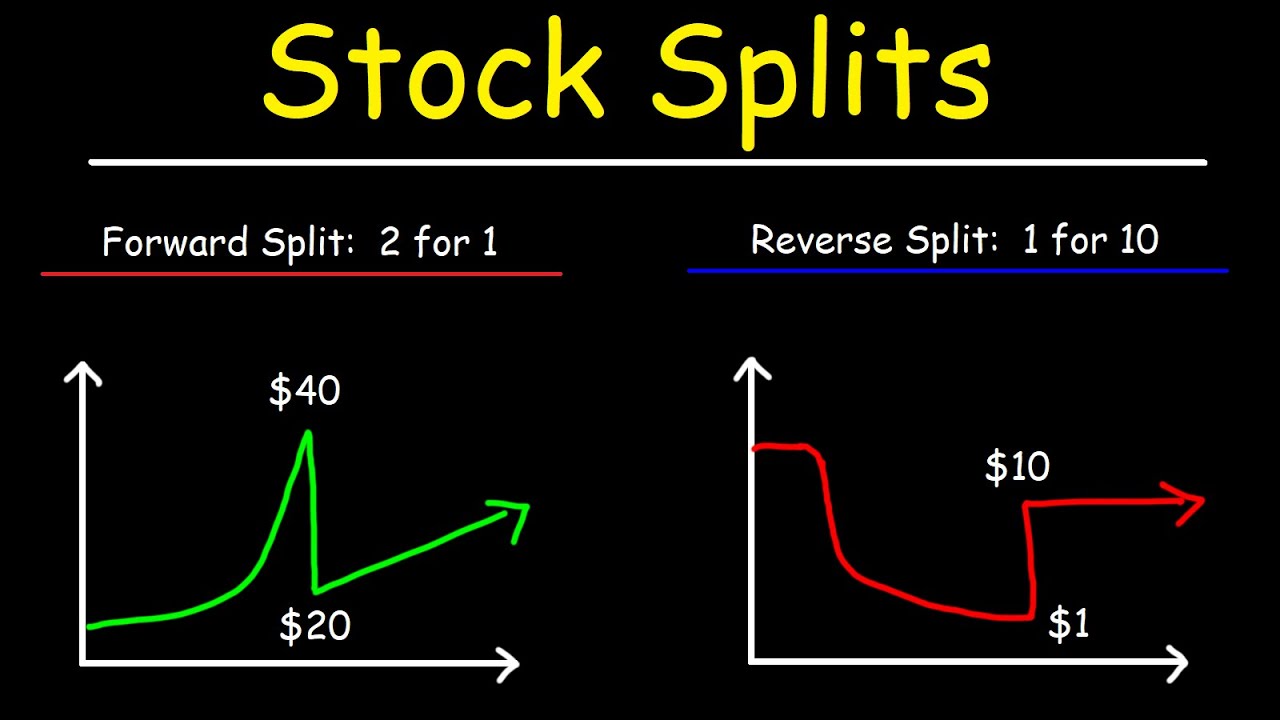
In a reverse stock split, a company reduces the total number of its outstanding shares, which increases the share price proportionately. For example, in a 1-for-10 reverse stock split, shareholders would receive one new share for every ten shares they owned, resulting in a tenfold increase in the share price. While this might sound beneficial, reverse stock splits can signal underlying issues within a company.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the reasons behind reverse stock splits, their implications for shareholders, and how they can affect a company's market perception. Whether you are an investor looking to understand this concept or a finance enthusiast wanting to broaden your knowledge, this article will provide valuable insights.
Table of Contents
- What is Reverse Stock Split?
- Why Do Companies Conduct Reverse Stock Splits?
- Impact on Shareholders
- Market Perception and Reverse Stock Splits
- Examples of Reverse Stock Splits
- Benefits and Drawbacks of Reverse Stock Splits
- Reverse Stock Split vs. Regular Stock Split
- Conclusion
What is Reverse Stock Split?
A reverse stock split is a process by which a company consolidates its shares to reduce the total number of outstanding shares while increasing the share price. This is typically done to meet listing requirements of stock exchanges or to improve the company’s market image. The key aspects of reverse stock splits include:
- Reduction in the number of shares: For example, in a 1-for-5 reverse stock split, every five shares owned will be converted into one share.
- Proportional increase in share price: The share price increases proportionately, ensuring that the overall market capitalization remains unchanged.
- No change in shareholder equity: Although the number of shares decreases, the value of each share increases, keeping the total value of shares owned by a shareholder the same.
Why Do Companies Conduct Reverse Stock Splits?
Companies may choose to conduct a reverse stock split for several reasons, including:
- Compliance with stock exchange requirements: Many stock exchanges have minimum price requirements for listed shares. If a company's share price falls below this threshold, it risks being delisted.
- Improving market perception: A higher share price post-split may improve the company's image, making it more attractive to institutional investors who may have restrictions on investing in penny stocks.
- Consolidating ownership: Reverse stock splits can help reduce the number of shareholders, which may simplify decision-making processes for management.
- Attracting new investors: Companies believe that a higher stock price might attract new investors and potentially lead to increased demand for shares.
Impact on Shareholders
The impact of a reverse stock split on shareholders can vary, but here are some common effects:
- Value preservation: The total value of shareholders' investments typically remains the same immediately after the split.
- Potential loss of confidence: Reverse stock splits can be viewed negatively, as they may indicate financial distress, leading to a loss of confidence among existing investors.
- Changes in trading behavior: Higher stock prices may lead to changes in the trading behavior of some investors, potentially impacting liquidity.
Market Perception and Reverse Stock Splits
Market perception plays a significant role in the effectiveness of reverse stock splits. Here are some factors to consider:
- Investor sentiment: A reverse stock split can be perceived as a sign of weakness, causing negative sentiment among investors.
- Long-term vs. short-term effects: While the immediate effects may not be drastic, over time, the company's performance post-split can significantly influence market perception.
- Communication strategies: How a company communicates the reasons for the reverse stock split can impact how investors respond.
Examples of Reverse Stock Splits
Several high-profile companies have undergone reverse stock splits. Here are a few notable examples:
- Citigroup (C): In 2011, Citigroup executed a 1-for-10 reverse stock split to stabilize its stock price after the financial crisis.
- Marble Arch Investments: This company conducted a reverse stock split in 2020 to meet the minimum price requirements of its listing.
- Abercrombie & Fitch (ANF): In 2014, Abercrombie & Fitch announced a 1-for-5 reverse stock split as part of its strategy to enhance shareholder value.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Reverse Stock Splits
Benefits
- Improved stock price stability
- Increased appeal to institutional investors
- Meeting exchange listing requirements
Drawbacks
- Negative perception among investors
- Potential loss of liquidity
- Possibility of further declines in stock prices post-split
Reverse Stock Split vs. Regular Stock Split
While both reverse stock splits and regular stock splits involve changes to the number of outstanding shares, they serve different purposes:
- Regular stock split: A regular stock split increases the number of shares and decreases the price per share, typically to make shares more affordable and attract a broader base of investors.
- Reverse stock split: A reverse stock split reduces the number of shares while increasing the price per share, often to comply with exchange regulations or improve market perception.
Conclusion
In conclusion, reverse stock splits serve as a strategic tool for companies looking to enhance their market presence and comply with exchange requirements. However, the implications for shareholders can be mixed, as investor perception plays a crucial role in the outcome. Understanding the dynamics of reverse stock splits is essential for any investor looking to navigate the complexities of the stock market effectively.
If you found this article helpful, please consider leaving a comment below, sharing it with others, or exploring other articles on our site for more insights into finance and investing.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here for more informative content!
Citi Stock: An In-Depth Analysis Of Citigroup's Stock Performance
Burt Reynolds Relationships: A Deep Dive Into His Love Life
Michelle Troconis: A Deep Dive Into Her Life And Influence